Power Reality: Assessing The Actual Energy Demand Of A Modern Household
Understanding your home's true energy requirements becomes crucial when selecting backup power solutions. Modern households rely on an intricate web of electrical devices, from essential lighting and refrigeration to sophisticated electronics and appliances. Calculating actual power consumption helps determine the right generator capacity, fuel type, and operational strategy for maintaining comfort and safety during outages.

Modern households consume electricity in complex patterns that vary throughout the day and across seasons. Understanding these consumption patterns becomes essential when evaluating backup power needs and selecting appropriate generator systems for emergency preparedness.
Compact Generator Solutions for Essential Electronics
The compact one kilowatt gasoline unit with a fifty cubic centimeter engine represents the entry point for emergency power generation. These lightweight systems, typically weighing under fifteen kilograms, provide quick deployment capabilities for essential household lighting and mobile device charging. A fuel consumption rate of zero point five liters per hour at half load makes these units economical for short-term outages, maintaining connectivity through the simple ritual of keeping the smallest electronics active during localized power shifts.
These portable units excel at powering LED lighting systems, smartphone chargers, small radios, and basic communication devices. Their compact design allows for easy storage in garages or utility rooms, ready for immediate deployment when grid power fails.
Mid-Range Power Solutions for Office Equipment
The two kilowatt peak power rating with integrated inverter technology delivers stable electrical flow suitable for sensitive office electronics. Modern inverter generators maintain total harmonic distortion under three percent, protecting computers, printers, and networking equipment from power quality issues. Eco mode operation keeps acoustic noise levels below sixty decibels, while parallel ports allow combining separate units for additional digital support.
These systems effectively maintain home router and laptop connectivity without noticeable flicker, enabling remote work capabilities during extended outages. The clean power output protects valuable electronics from voltage fluctuations that could cause permanent damage.
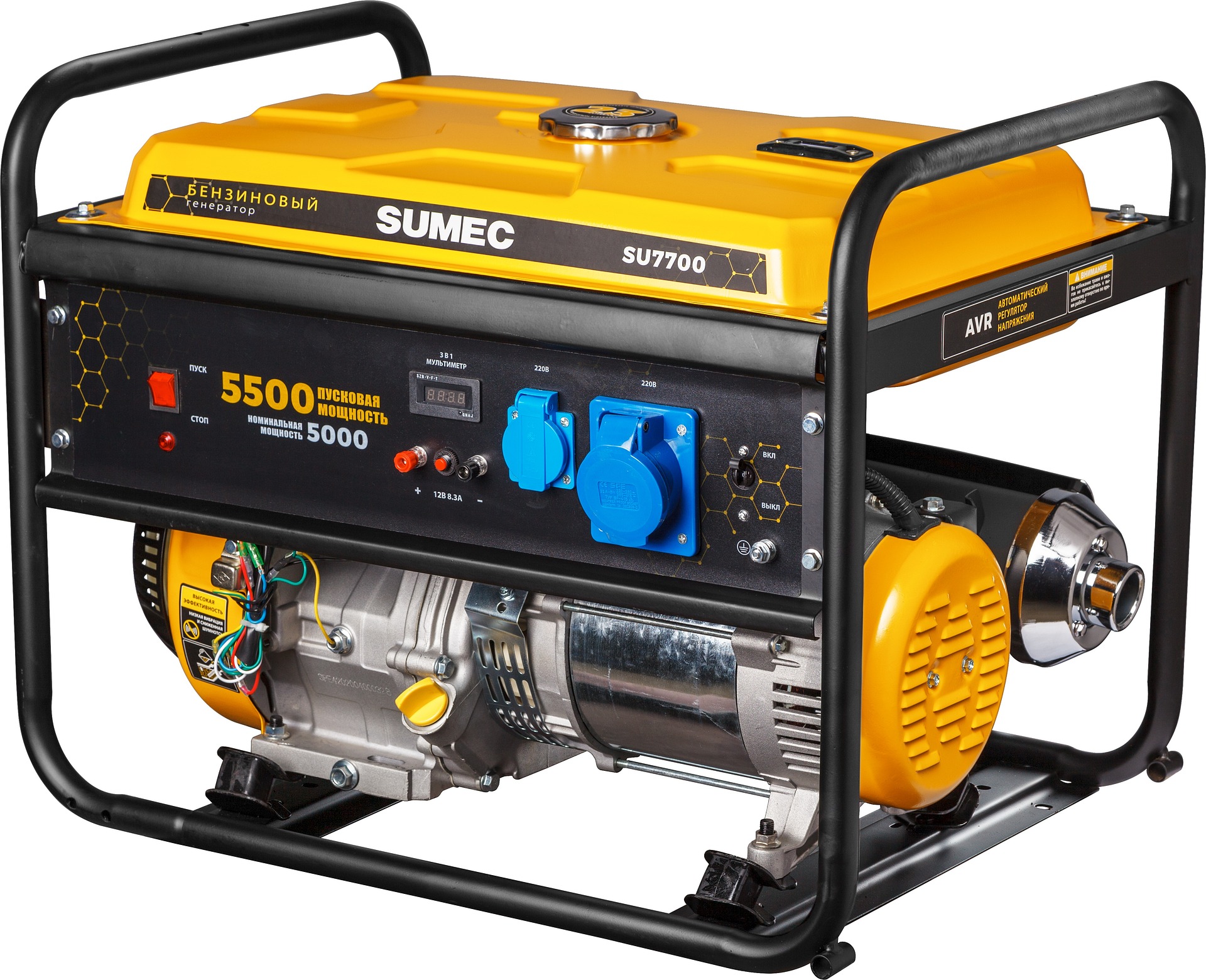
Heavy-Duty Generators for Kitchen Appliances
The three to five kilowatt tier handles heavy kitchen appliance loads, including the specific surge wattage required for induction motor refrigerator cycles. These generators must accommodate starting currents that can be three to five times the running wattage of major appliances. Gasoline fuel shelf life considerations become important compared to the stability of diesel fuel options for longer-term storage.
A twelve volt electric start mechanism with integrated battery eliminates manual pull-starting, crucial for maintaining food safety and family comfort during extended power interruptions. These systems can operate refrigerators, freezers, microwave ovens, and electric water heaters simultaneously.
Whole-House Generator Systems
The ten kilowatt liquid cooled multi cylinder diesel engine system provides continuous reliability for comprehensive home backup power. An automatic transfer switch enables hands-free transition from the main grid, detecting outages within seconds and restoring power automatically. External fuel tanks support extended multi-day power stability, while weatherproof sound enclosures allow permanent outdoor placement near garden areas.
These sophisticated systems integrate seamlessly with home electrical panels, powering heating and cooling systems, water pumps, security systems, and all household circuits simultaneously.
| Generator Type | Power Output | Engine Type | Fuel Consumption | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Gasoline | 1-2 kW | Single Cylinder | 0.5-0.8 L/hour | $300-$800 |
| Inverter Generator | 2-4 kW | 4-Stroke Engine | 0.3-0.6 L/hour | $500-$1,500 |
| Mid-Range Portable | 3-5 kW | OHV Engine | 0.8-1.2 L/hour | $800-$2,000 |
| Standby Generator | 7-20 kW | Multi-Cylinder | 1.5-3.0 L/hour | $2,500-$8,000 |
| Whole-House System | 20+ kW | Liquid Cooled | 2.0-4.0 L/hour | $5,000-$15,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Integration and Maintenance Considerations
The generator system becomes a natural extension of home architecture when properly planned and installed. Scheduled oil change intervals and air filter maintenance logs ensure long-term reliability, while acoustic isolation strategies help dampen mechanical vibrations through floor mounting systems.
Modern homes maintain their identity despite neighborhood power failures through well-designed backup power infrastructure. A house equipped with appropriate generator capacity demonstrates self-reliance through carefully planned unseen infrastructure that activates automatically when needed.
Regular maintenance schedules include monthly test runs, seasonal fuel system checks, and annual professional inspections. Proper installation considers local building codes, noise ordinances, and utility interconnection requirements for automatic transfer systems.
Selecting the right generator capacity requires careful analysis of actual household energy consumption patterns, peak demand periods, and essential versus non-essential loads. Professional energy audits can identify specific power requirements and help optimize generator sizing for both economic efficiency and reliable operation during extended outages.